Reviewed by Dr Bing Zhu (Internal Medicine Specialist)
What is canine Cushing’s disease?
Canine Cushing’s disease, just like Cushing’s disease in all species, is a hormonal disease that can occur in humans, dogs, and cats. Known medically as hyperadrenocorticism, canine Cushing’s disease has multiple causes, which all lead to excessive production of cortisol hormone by the adrenal glands (located just above the kidneys).
Known commonly as the “stress hormone”, cortisol is a steroid hormone responsible for managing the body’s physiological response to stress or danger. It plays a role in regulating energy use, blood pressure, intestinal health, liver function, and the immune system among other things. The body requires cortisol to function properly. However, prolonged periods of excessive cortisol levels can have damaging effects.
What are the symptoms of canine Cushing’s disease?
Canine Cushing’s disease can cause many varied signs, but different patients will exhibit different signs, not necessarily showing all signs at once. Changes noted by dog owners include increased drinking and urination, increased appetite, increased panting, reduced activity, and a potbelly. Patients can often have several skin related problems, such as reoccurring infections, thin skin, and poor/change in coat condition and colour.
What causes canine Cushing’s disease?
Canine Cushing’s disease has three root causes. Up to 90% of cases result from a tumour in the pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain). The tumour causes the pituitary gland to release too much of the ACTH hormone, which in turn results in an overproduction of cortisol from the adrenal glands.
An alternative cause of Cushings is a tumour on the adrenal gland itself, causing an overproducing of cortisol.
A third cause of Canine Cushing’s disease is administration of steroid medication (either oral or topical), prescribed by a veterinarian to manage other diseases in the body. We do not test for canine Cushing’s disease in patients on steroid medication because the Cushing’s is likely from the medications.
How is canine Cushing’s disease diagnosed?
If your dog is suspected of having canine Cushing’s disease, your local vet or an Internal Medicine Specialist can diagnose canine Cushing’s disease through running a number of different blood tests. In isolation, no single test can confirm or rule out Cushing’s (some patients require 2 to 4 different tests), but a Medicine Specialist would be best able to interpret the test results in light of the signs your dog is showing to decide whether Cushing’s is a likely diagnosis.
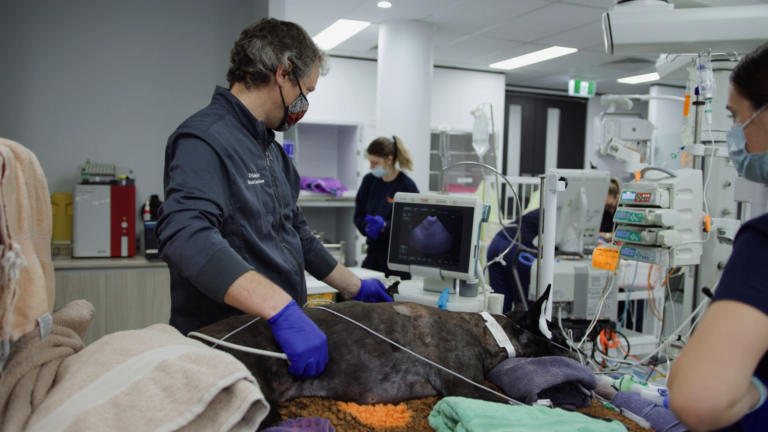
After diagnosis, additional scans (eg. ultrasound and/or CT) may be used to assess the size and impacts of the tumours causing the Cushing’s. At SASH, these are performed by specialists vets, such as Diagnostic Imaging Specialists.
How is canine Cushing’s disease treated?
At SASH, we are fortunate to be able to offer more treatment options for canine Cushing’s disease than anywhere else in the country, to ensure all options can be explored in the best interest of the dog and their family. The type of treatment will differ depend on the cause of the disease, and the individual circumstances of you and your pet. Your SASH Specialist will be able to explain the pros, cons, and suitability of each of the treatment options to help you make the most informed decision.
No treatment
Canine Cushing’s is not always life threatening. In some cases, a decision is actually made not to treat the Cushing’s disease if it is reducing the impact of other diseases, or if no treatment is better for the dog’s quality of life.
Uncommonly, if Cushing’s is not causing problems to the dog and the cost of drugs or veterinary assessment is too expensive, it can be appropriate to monitor a pet. This is something a SASH Internal Medicine Specialist would be able to assess and help guide you to make the best decision for your dog.
Medical management
Some cases of canine Cushing’s disease respond well to medical management. These cases are overseen by an Internal Medicine Specialist, who will provide a combination of drugs to help regulate the affected hormones to within normal levels. Medical management can be tricky, with the risk of drug side effects. It is therefore important to have a specialist oversee the case. Although on-going medications, blood tests, and check-ups will be required, the quality of life for the pet can be good.
If the Cushing’s is caused by overuse of cortisone drugs for other diseases, this can also be medically managed by an Internal Medicine Specialist. Internal Medicine Specialists are ideal for these cases as they are experts in managing multiple simultaneous medical diseases.
Surgery
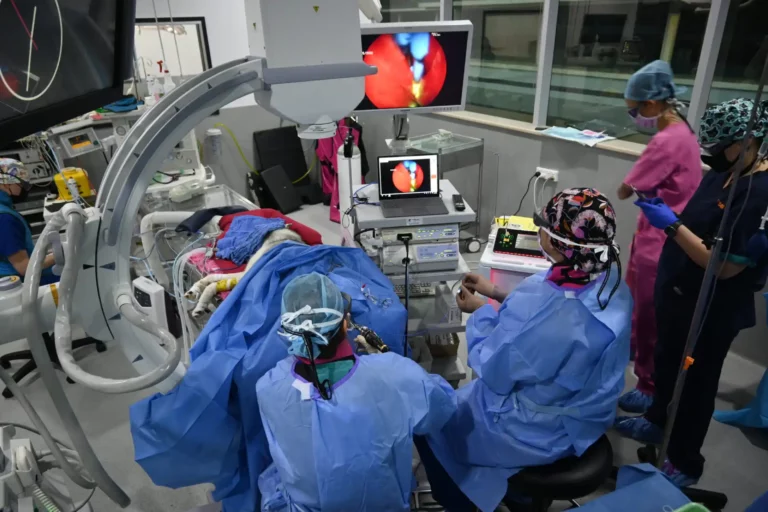
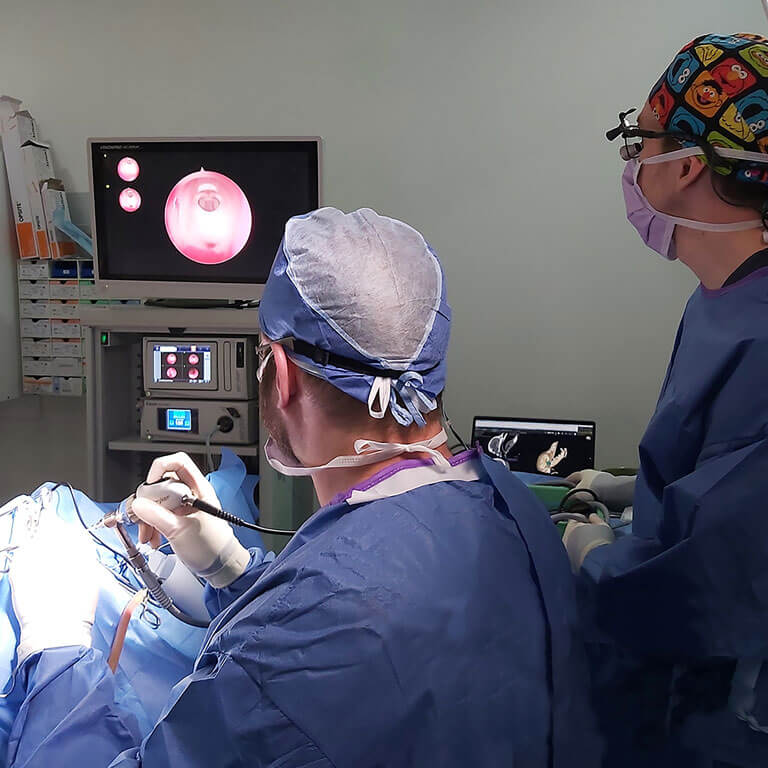
Surgery can also be presented as a treatment option for some cases. They aim to “cure” the disease by removing the affected organ that is causing the Cushing’s. If the tumour is located on the pituitary, SASH is one of the few places in the world, and the only place in Australia to offer the pituitary surgery with a Specialist Neurosurgeon working together with Internal Medicine and Critical Care Specialists through the Pituitary Centre.

If the tumour is located on the adrenal gland, this delicate surgery can be performed by SASH Specialist Surgeons.
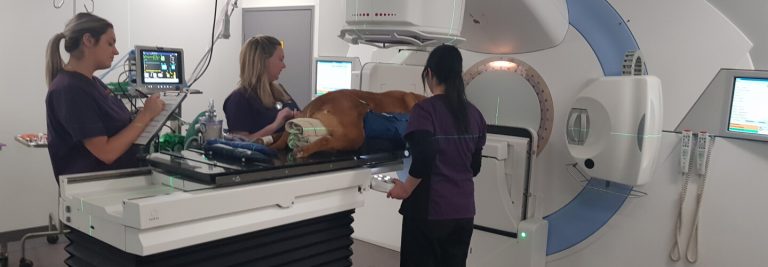
Radiation therapy
Finally, when pituitary surgery is not an option, radiation therapy through the Radiation Oncology department may also be used to reduce the size of the tumour.
Canine Cushing’s disease outcomes
The outcome of treating canine Cushing’s disease can be very positive for your dog, depending on the severity and spread of the tumor, and how it is managed/treated. If you suspect your dog has Cushing’s, ask your local vet for a referral to SASH.
Call us to book a consult by clicking the contact button below.